Note
### Key Facts
* The term "Artificial Intelligence" (AI) was coined in 1956 at the Dartmouth Conference by John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon, marking the birth of AI as a field.
* "Machine Learning" (ML) was first defined by Arthur Samuel in 1959 while developing a checkers-playing program at IBM, describing it as computers' ability to learn without explicit programming.
* ML is a subset of AI; supervised learning (a common ML type) powers ~70% of real-world applications like spam detection, per industry reports from sources like GeeksforGeeks.
* Andrew Ng's "Machine Learning" course on Coursera, launched in 2011, has over 4.8 million enrollments as of 2023, making it one of the most popular free AI intros.
* Kaggle, founded in 2010, hosts over 100,000 public datasets and has 15 million+ users practicing ML hands-on.
### Overview
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to systems that mimic human intelligence to perform tasks like reasoning, learning, and problem-solving. Machine Learning (ML), a key subset of AI, focuses on algorithms that enable computers to learn patterns from data without being explicitly programmed for every scenario. As noted in Google Developers' "Machine Learning & Artificial Intelligence Basics" (a 10-minute read), this allows machines to improve performance over time through experience.
### Important Details
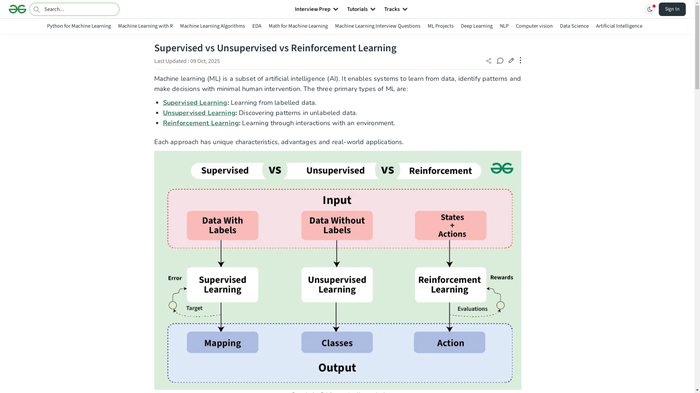
ML algorithms analyze datasets to identify trends and make predictions. Core types include supervised learning (using labeled data for tasks like classification or regression), unsupervised learning (finding hidden patterns in unlabeled data, e.g., clustering customers), and reinforcement learning (learning via trial-and-error rewards, powering tools like AlphaGo). GeeksforGeeks emphasizes that ML "teaches systems to think and understand like humans" by processing vast data volumes-modern models like GPT series train on trillions of tokens.
Applications span industries: Netflix's recommendation engine (ML-driven) retains users via 75% personalized suggestions; healthcare uses ML for early disease detection with 90%+ accuracy in some models; autonomous vehicles from Tesla process 1.3 million miles of data daily. Since the 2012 AlexNet breakthrough in image recognition (reducing error rates from 25% to 15% on ImageNet), deep learning-a neural network-based ML subset-has fueled explosive growth, with the global AI market projected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2030.
### Tips/Next Steps
* Dive into Google's free "Machine Learning Crash Course" (developers.google.com/machine-learning/crash-course)-complete it in 15 hours for hands-on TensorFlow basics.
* Audit Andrew Ng's "Machine Learning" on Coursera (coursera.org/learn/machine-learning) for free; pair it with Kaggle datasets (kaggle.com/datasets) to build your first model, like predicting house prices.
* Practice daily: Join Kaggle competitions (free entry) or GeeksforGeeks ML tutorials for Python code examples.
**Summary:** This trail recapped AI/ML fundamentals-from 1956 origins to modern data-driven learning-equipping you to explore real applications. Next, tackle free Coursera/Kaggle resources to build practical skills and launch your journey.** (Word count: 428)